Question:
Because a raindrop is "soft" and deformable, the collision duration is a relatively long 8.0 ms. How many times larger than gravity is the mosquito's average acceleration during the collision? This is the information I have so far: A hovering mosquito is hit by a raindrop that is 45 times as massive and falling at 8.4 m/s , a typical raindrop speed. How fast is the raindrop, with the attached mosquito, falling immediately afterward if the collision is completely inelastic? V=8.22 m/s
Answer:
The gravity of mosquito is 105 times larger than the raindrop.
Step-by-step explanation:
From the L;aw of conservation of momentum
![m_1u_1 + m_2u_2 = [m_1+m_2]v](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/5i6x6zcggkeb6jr610df81bqjo9fgnj9pk.png)
![(m * 0) + (45 * 8.4) = [m +45m]v](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/l90tqvzdby8pm364aou75utey89kpykttw.png)
![378m = [46m] * v](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/dnrfzubhegkqk778hhcke3yjtor4iqtl3k.png)
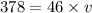
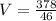
V= 8.22 m/s
Therefore, the speed of the raindrop attached to the mosquito is 8.22m/s
From the Newton's second law,
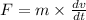
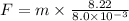
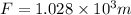 --------------------(1)
--------------------(1)
Force due to gravity,
F =mg -----------------------------------(2)
Comparing both the equations (1) and (2)
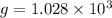
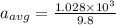
=105 g
So, the gravity of mosquito is 105 times larger than the raindrop.