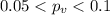Answer:
a)
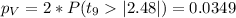
We can use the following excel code: "=2*(1-T.DIST(2.48,9,TRUE))"
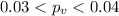
b)
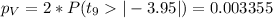
We can use the following excel code: "=2*(1-T.DIST(3.95,9,TRUE))"
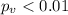
c)
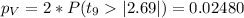
We can use the following excel code: "=2*(1-T.DIST(2.69,9,TRUE))"
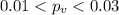
d)
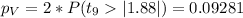
We can use the following excel code: "=2*(1-T.DIST(1.88,9,TRUE))"
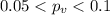
Explanation:
For this case we are testing the following system of hypothesis:
Null hypothesis:
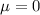
Alternative hypothesis:
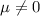
The sample size is n=10, so then the degrees of freedom are given by:
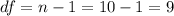
In order to calculate the p value we can use the fact that we are conducting a bilateral test so then the p value is given by:
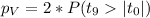
Where
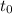 represent the calculated or observed statistic.
represent the calculated or observed statistic.
a) t0= 2.48
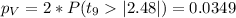
We can use the following excel code: "=2*(1-T.DIST(2.48,9,TRUE))"
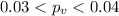
b) t0= -3.95
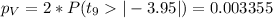
We can use the following excel code: "=2*(1-T.DIST(3.95,9,TRUE))"
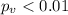
c) t0=2.69
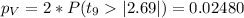
We can use the following excel code: "=2*(1-T.DIST(2.69,9,TRUE))"
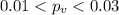
d) t0=1.88
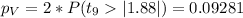
We can use the following excel code: "=2*(1-T.DIST(1.88,9,TRUE))"