Answer: A.gamma rays, X rays, ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, radio
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's begin by explaining that electromagnetic radiation is divided in a set known as electromagnetic spectrum, and is distributed in its different wavelengths.
So, if we go from the shortest to the longest wavelengths known up to now (since the electromagnetic spectrum is infinite and continuous), we will have the following:
Gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet, visible light (all the colors we are able to see), infrared, radio waves.
Let's make a brief of them:
-Gamma rays: With a wavelength in the order of
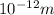 , is a type of ionizing radiation capable of penetrating matter quite deeply and is able to cause serious damage to the nucleus of the cells.
, is a type of ionizing radiation capable of penetrating matter quite deeply and is able to cause serious damage to the nucleus of the cells.
-X rays: With a wavelength between
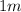 and
and
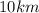 . It is invisible to the human eye, capable of crossing opaque bodies.
. It is invisible to the human eye, capable of crossing opaque bodies.
-Ultraviolet light: Whose wavelength is approximately between 100 nm and 380 nm; is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is not visible to the human eye.
-Visible light: This part of the spectrum is located between ultraviolet light and infrared light (380 nm - 780 nm). This is the only portion of the spectrum that is visible to humans, since the receptors in our eyes are only sensitive to these wavelengths.
-Infrared: This type of radiation is not visible to the human eye, since its wavelengths are outside the visible spectrum (between 700 nm and 1 mm).
This light has many uses, including heating lamps in physiotherapy and medical treatments, heat sensing devices, among others.
-Radio waves: These are a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 10 m to 10,000 m. This radiation is useful to transport information and is important in telecommunications.