Answer: Option (A) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the ideal gas law, the formula is as follows.
PV = nRT
And, when the temperature is constant then,
PV = constant
This means that P is inversely proportional to V in this case . Therefore, if the volume is doubled than pressure would be half as large.
Mathematically,
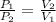
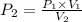
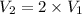
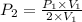
=
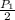
This means that
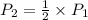
Thus, we can conclude that if the volume of a confined gas is doubled, while the temperature remains constant, then pressure would be half as large.