Answer:
The force of gravity after you double the mass and the distance is half of the initial force:
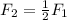
Step-by-step explanation:
The initial force of gravity is:
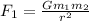
where
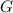 is the universal gravitational constant,
is the universal gravitational constant,
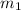 is the mass of the first object,
is the mass of the first object,
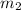 is the mass of the second object, and
is the mass of the second object, and
 is the distance between the objects.
is the distance between the objects.
If the mass of the second object is doubled, now we have
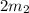 , and if the distance between the objects is also doubled instead of
, and if the distance between the objects is also doubled instead of
 now we have
now we have
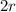 .
.
So the force of gravity now is:
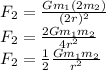
and we know that
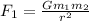
so the new force of gravity is:
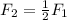
The force of gravity after you double the mass and the distance is half of the initial force.