Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction equation is as follows.
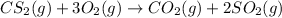
This means that 1 mole of
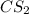 reacts with 3 moles of
reacts with 3 moles of
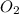 and gives 1 mole of
and gives 1 mole of
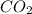 and 2 moles of
and 2 moles of
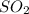 .
.
Now, let us assume that there are x moles of
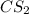 and y moles of
and y moles of
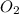 . According to the ideal gas equation, we have PV = nRT.
. According to the ideal gas equation, we have PV = nRT.
where, p = pressure, V = volume, n = no of moles, R = Universal gas constant, and T = temperature.
Expression for total pressure is as follows.
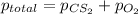
=
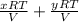
=
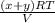 ........ (1)
........ (1)
The given data is as follows.
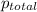 = 3 atm, R = 0.0821 L atm/mol K, T = 300 K, V = 10 L
= 3 atm, R = 0.0821 L atm/mol K, T = 300 K, V = 10 L
Now, using equation (1)
x + y =
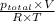
=
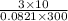 mol
mol
= 1.218 mol ......... (2)
Again, when the reaction from x moles of
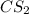 , x moles of
, x moles of
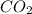 and 2x moles of
and 2x moles of
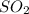 are produced. During this process 3x moles of
are produced. During this process 3x moles of
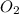 are consumed as per the above reaction.
are consumed as per the above reaction.
Therefore, after the reaction,
moles of
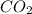 = x ,
= x ,
moles of
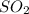 = 2x ,
= 2x ,
moles of
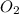 = (y - 3x)
= (y - 3x)
and,
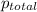 = 2.4 atm
= 2.4 atm
Hence, again the value of
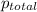 is as follows.
is as follows.
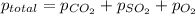
=
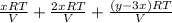
=
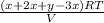
=
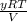
Hence, the value of y can be calculated as follows.
y =
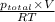
=
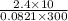 mol
mol
= 0.974 mol .......... (3)
On solving both equations (2) and (3), we find out the value of x as 0.244 moles.
As the molecular weight of
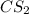 is 76 g/mol. Now, calculate the mass of
is 76 g/mol. Now, calculate the mass of
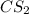 originally present as follows.
originally present as follows.
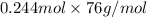
= 18.544 g
Thus, we can conclude that the mass (in grams) of
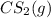 originally present is 18.544 g.
originally present is 18.544 g.