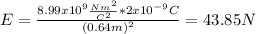Answer:
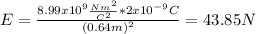
Step-by-step explanation:
For this case we assume that we want to find the electrical field at the point P as we can see on the figure attached.
The electrical field wormula is given by:
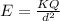
Where r is the distance from the point and the charge. On this case we can use the Pythagoras theorem and we got:
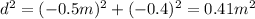
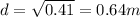
And now we can replace into the formula since we know that
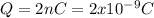 and
and
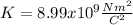 , and we got:
, and we got: