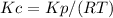Answer:
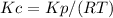
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following chemical equilibrium:
CaCO₃(s) ⇄ CaO(s) + CO₂(g)
Given the pressure equilibrium constant Kp = pCO₂
We can calculate the concentration equilibrium constant (Kc) using the following expression.
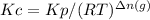
where,
R is the ideal gas constant
T is the absolute temperature
Δn(g) = moles of gaseous products - moles of gaseous reactants = 1 - 0 = 1
The expression for this reaction is: