Answer: The molar solubility of nitrogen gas when pressure is increased is 0.042 mol/L
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Solubility of nitrogen gas in water = 56.0 mg/100 g
Or, solubility of nitrogen gas in water = 0.056 g/100 mL (Density of water = 1 g/mL & Conversion factor used: 1 g = 1000 mg)
Solubility of a solute is defined as the moles of solute dissolved in 1 L of solvent.
Conversion factor used: 1 L = 1000 mL
Applying unitary method:
In 100 mL water, the amount of solute (nitrogen gas) dissolved is 0.056 grams
So, in 1000 mL of water, the amount of solute (nitrogen gas) dissolved will be =
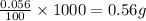
Converting this solubility into mol/L by dividing with the molar mass of nitrogen gas:
Molar mass of nitrogen gas = 28 g/mol
So, Solubility of nitrogen gas =
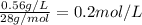
To calculate the Henry's constant we use the equation given by Henry's law, which is:
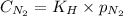 .........(1)
.........(1)
where,
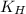 = Henry's constant
= Henry's constant
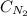 = molar solubility of nitrogen gas = 0.02 mol/L
= molar solubility of nitrogen gas = 0.02 mol/L
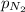 = partial pressure of nitrogen gas = 2.38 atm
= partial pressure of nitrogen gas = 2.38 atm
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
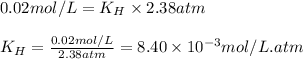
When pressure is changed to 5.00 atm
Now,
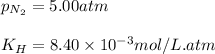
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
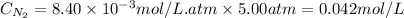
Hence, the molar solubility of nitrogen gas when pressure is increased is 0.042 mol/L