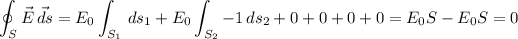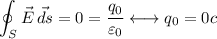Answer:
The charge inside the cube is null.
Step-by-step explanation:
If we apply the gauss theorem with a cubical gaussian surface of the size of the cube:
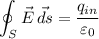
If we consider than the direction of the electric field is
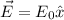 , we can solve the problem differentiating the integral for each face of the cube:
, we can solve the problem differentiating the integral for each face of the cube:
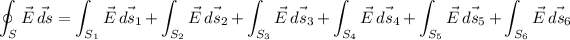
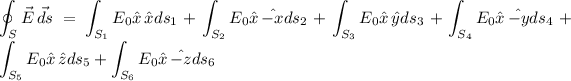
E₀ is a constant and each surface is equal to each other, so:
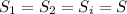
Therefore: