Answer:
HCl is limiting reactant.
The maximum volume of the 2.4 moles of carbon dioxide at STP is 53.76 L.
Step-by-step explanation:
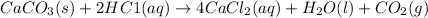
Moles of calcium carbonate = 2.5 moles (given)
According to reaction, 1 mole of calcium carbonate react with 2 moles of HCl. then 2.5 moles of calcium carbonate will react with:
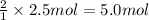 of HCl
of HCl
Moles of hydrochloric acid = 4.8 moles (given)
According to reaction, 2 mole of HCl react with 1 moles of calcium carbonate. Then 4.8 moles of HCl will react with:
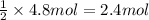 of calcium carbonate
of calcium carbonate
As we can see that HCl is completely reacting with 2.4 moles of calcium carbonate.Hence HCl is limiting reagent .Also, the moles of carbon dioxide gas will depend upon moles of HCl.
According to reaction, 2 moles of HCl gives 1 mole of carbon dioxide gas. then 4.8 moles of HCl will give:
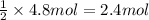 of carbon dioxide gas.
of carbon dioxide gas.
To calculate volume of carbon dioxde gas at :
1 mole of ideal gas occupies 22.4 L of volume at STP.
Then 2.4 moles of carbon dioxide will occupy :
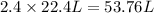
The maximum volume of the 2.4 moles of carbon dioxide at STP is 53.76 L.