Answer:
The resistivity of metals decreases on increase in temperature whereas the resistivity of semiconductors increases with increase in temperature.
Step-by-step explanation:
The majority charge carriers in metals are electrons which are explained by the electron-sea model. The electron sea model considers metal to have a sea of conducting electrons in between the nucleus arrangement.
The nucleus is bind firmly within the lattice structure and when the temperature has increased this accounts for the lattice vibrations as a result offering obstructions to the valence electrons which increases its bulk resistivity.
The variation in the resistivity of metal is given by:
![\rho=\rho_0[1+\alpha_t(T-T_0)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/ol2nygfr3kh6x1oykabguogukx1wsu9m0n.png)
where:
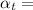 temperature coefficient of resistivity which is defined as the fractional change in resistivity per unit change in temperature.
temperature coefficient of resistivity which is defined as the fractional change in resistivity per unit change in temperature.
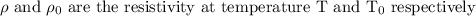
At temperatures 500 K above the room temperature we have the variation of resistivity of the metal in a linear manner.
- For semiconductors, the value of coefficient of resistivity is negative which implies that the resistivity of semiconductors decreases as temperature increases.