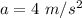Answer:
The acceleration of the particle at any time t
Explanation:
Given:
The position of a particle moving in a straight line at any time t is.
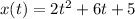
The velocity of the particle
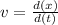
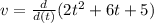
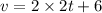
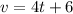
So the velocity of the particle
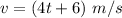
The acceleration of the particle
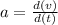
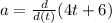
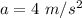
In this condition the acceleration does not depending upon the time, so the acceleration is constant
Therefore the acceleration of the particle at any time t