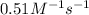Answer : The value of the constant for a second order reaction is,
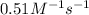
Explanation :
The expression used for second order kinetics is:
![kt=(1)/([A_t])-(1)/([A_o])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/tlg6nth7imx9pwjb4oksbydlkeyozanniz.png)
where,
k = rate constant = ?
t = time = 17s
![[A_t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c6se0yk0a5jz0ud2m1a9jh5tv0rk9jx59i.png) = final concentration = 0.0981 M
= final concentration = 0.0981 M
![[A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/3jrctnxyrdjmiz9ngr0s6o9r3hdvpo6qhe.png) = initial concentration = 0.657 M
= initial concentration = 0.657 M
Now put all the given values in the above expression, we get:
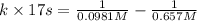
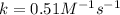
Therefore, the value of the constant for a second order reaction is,