Step-by-step explanation:
It is known that the molecular weight of
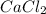 is 111 g/mol. This means that 1 mole of
is 111 g/mol. This means that 1 mole of
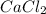 contains 111 g
contains 111 g
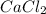 .
.
1 g
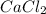 =
=
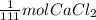
As we know that the density of water is 1 g/cc (as 1 ml = 1 cc).
So, 100 ml water = 100 g water. Therefore, in 100 g of water
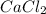 present will be calculated as follows.
present will be calculated as follows.
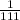 mol
mol
So, in 1000 g water the amount of
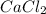 present will be calculated as follows.
present will be calculated as follows.
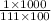
= 0.09 mol
Hence, the molality of
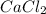 is 0.09 mol.
is 0.09 mol.
According to Raoult's law,
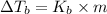
where,
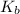 = boiling point constant
= boiling point constant
For pure 1 kg water,
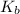 = 0.52 K.kg/mol
= 0.52 K.kg/mol
m = molality of solution
Therefore, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
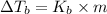
=
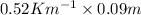
= 0.0468 K
Therefore, the boiling point will raise by 0.0468 K.