Answer:
Integral doesn't converge
Explanation:
In order to computed the improper integral replace infinite limit with a finite value:
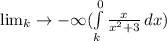
For the integrand
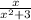 substitute:
substitute:
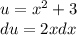
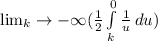
The integral of 1/u is log(u):
Applying the fundamental theorem of calculus and substituing back for u=x^2 +3:
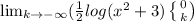
Evaluating the limits:
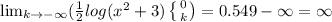
Hence, the integral doesn't converge