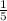Answer:
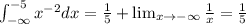
Because the
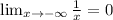
The integral converges to
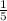
Explanation:
For this case we want to find the following integral:
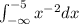
And we can solve the integral on this way:
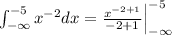
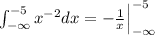
And if we evaluate the integral using the fundamental theorem of calculus we got:
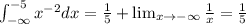
Because the
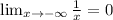
The integral converges to