Answer:
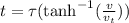
Step-by-step explanation:
Terminal velocity is the maximum velocity attained by a body when the net upward force on it is equal to the net downward force as it falls through a fluid from a certain height.
The time required to reach terminal velocity is infinite as the object never reaches absolute terminal velocity and always approaches terminal velocity.
The velocity
 of a falling object expressed in terms of terminal velocity
of a falling object expressed in terms of terminal velocity
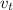 and time 't' is given as:
and time 't' is given as:
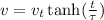
Where,
 is a constant and has units of time.
is a constant and has units of time.
Now, expressing the above in terms of time 't', we get:
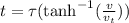
Therefore, the formula to find time to approach terminal velocity is:
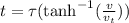
When the velocity is 76% of terminal velocity, the time taken is
 .
.
When the velocity is 96% of terminal velocity, the time taken is
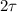 .
.
When the velocity is 99.5% of terminal velocity, the time taken is
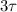 and so on..
and so on..