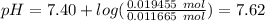Answer:
7.62
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the Henderson-Hasselbach equation, the pH value o a buffer can be calculated by the following equation:
![pH = pK_a + log(([A^-])/([HA]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/36y58r33ae9ipbcu9f6xnhhnx1ek020w9x.png)
Let's identify the variables:
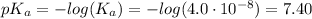
![[A^-] = [ClO^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/rsoffyflnhnkaplulo3unj0he7a9m1kkid.png)
![[HA] = [HClO]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/f27genzv9a0mq4cnmgja9pphpmkiwploio.png)
Identify the moles of each component:
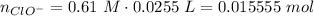
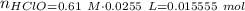
The strong base reacts with acid to produce more of the basic component:
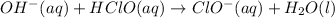
Hydroxide is the limiting reactant. The new amounts of the weak acid and base are:
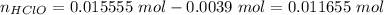
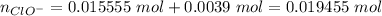
Let's use the molar amounts in the equation, as we have exactly same volume for each component in the buffer: