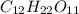Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the concentration of solute, we use the equation for osmotic pressure, which is:
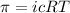
where,
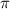 = osmotic pressure of the solution =
= osmotic pressure of the solution =
i = Van't hoff factor =
c = concentration of solute =
R = Gas constant =
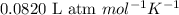
T = temperature of the solution = T
1) For 1 M
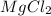 :
:
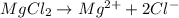
i = 3
c = 1 M
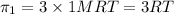
2) For 1 M
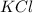 :
:
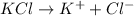
i = 2
c = M
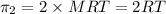
3) For 2 M
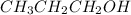 :
:
i = 1 ( organic molecule)
c = 2 M
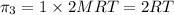
4) For 1 M
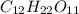 :
:
i = 1 ( organic molecule)
c = 1 M
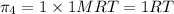
Osmotic pressures in decreasing order
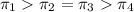
1 M
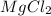 >1 M
>1 M
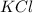 =2 M
=2 M
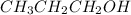 >1 M
>1 M