Answer:
The correct answer is: a 10% increase in the price of cantaloupes will increase the quantity demanded of water melons by 11%.
Step-by-step explanation:
The produce manager of a large grocery store is informed that the cross-price elasticity of demand between cantaloupes and water melons is 1.10.
The cross-price elasticity of demand is a measure to calculate the change in demand for a commodity due to a change in the price of another commodity.
It is calculated as a ratio of the percentage change in demand and percentage change in price.
A positive price elasticity implies that the two goods are substitutes. An increase in the price of one good leads to an increase in the demand for another.
The cross elasticity can be calculated as,
=
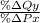
Let's assume that the price of cantaloupes increases by 10%.
Then,
1.10 =
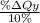
ΔQy = 11
So we see that a 10% increase in the price of cantaloupes will cause the demand for water melons to increase by 11%.