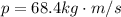´To develop this problem we will use the concepts related to the conservation of momentum and the application of energy conservation equations to find the velocity of the mass after the collision, like this:
Velocity of the mass
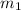 just before the collision
just before the collision
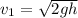
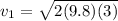
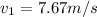
Therefore the momentum just before collision would be
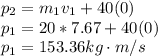
Momentum after the collision
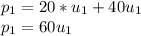
Since the momentum is conserved we have that
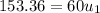
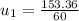
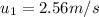
The velocity of mass
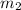 after the collision is given by
after the collision is given by
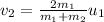
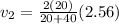
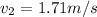
Therefore the change in momentum of mass 2 is
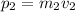
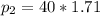
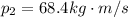
Therefore the impulse acting on m2 during the collision between the two boxes is