Answer:
216.7 ml
Step-by-step explanation:
Concentration
The concentration of a substance is defined as the quantity of solute existent in a given quantity of solution. Water is usually a liquid to add to the solute and produce the substance with the required concentration, often expressed in %, gr/ml or any other similar ratio. If the solute is expressed in units of mass and the solution is expressed in units of volume, then the concentration is known as mass concentration or density and is computed as
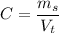
Where
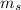 is the mass of solute and
is the mass of solute and
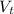 is the total volume of the solution
is the total volume of the solution
We know at first
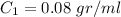
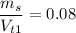
Operating
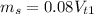
When we add 50 ml of water and keep the solute unchanged, we have
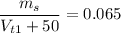
Or equivalently
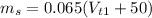
Equating both masses
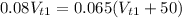
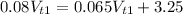
Rearranging and simplifying
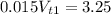
Solving
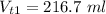
The mass of the solute is
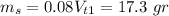
We don't know the density of the solute, so we cannot compute its volume which is part of the solution. If we neglect this volume because the concentration is small enough, we can say there were 216.7 ml of water in the initial solution.
If we estimate the density of the solute close to 1 gr/ml, the volume is 17.3 ml, and the initial volume of water in the solution is 216.7-17-3=199.4 ml