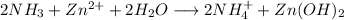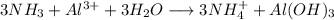Step-by-step explanation:
1) Amphoteric substances can react both like an acid or a base depending if they are in presence of a base or an acid.
Zinc hydroxide (Zn(OH)2):
In acid:
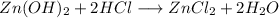
In base:
![Zn(OH)_2 + 2 NaOH \longrightarrow Na_2[Zn(OH)_4]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/xgfm296tnhfyl6bkvwqa9bixfkfvgzbf0m.png)
Aluminium hydroxide (Al(OH)3)
In acid:
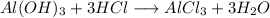
In base:
![Al(OH)_3 + NaOH \longrightarrow Na[Al(OH)_4]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/94ww811kphlsx8vrozcq2wcvagd1fdjhxg.png)
2) Reactions
a)
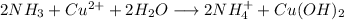
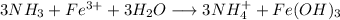
b)