Answer:
T = 5,06 10³ s
Step-by-step explanation:
For this exercise, let's use Newton's second law, where force is the force of gravitational attraction
F = m a
The acceleration is centripetal
a = v² / r
Let's replace
G m
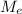 /
/
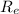 ² = m v² /
² = m v² /
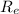
G
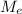 /
/
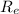 = v²
= v²
The velocity module is constant, so we can use the equation of uniform motion
v = d / t
Where the distance is the length of the circle and in this case the time is called the period
d = 2π
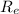
We replace
(2π
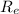 / T)² = G
/ T)² = G
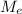 /
/
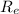
T² = 4π²
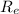 ³ / G
³ / G
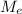
T = √ 4π²
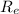 ³ / G
³ / G
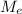
Let's calculate
T = √ (4π² (6.37 10⁶)³ / 6.67 10⁻¹¹ 5.98 10²⁴)
T = √ (255.83 10⁵) = √ (25.583 10⁶)
T = 5,05796 10³ s