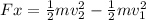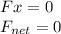Answer:
Work-Energy Theorem is that the work done on an object is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of that object:
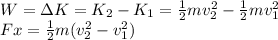
The relation between velocity and position is derived from the kinematics equations:
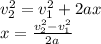
If we plug x into the work energy theorem, Newton's Second Law can be found:
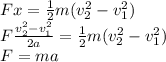
Newton's First Law is the law of inertia: If the net force on an object is zero, the acceleration of the object is also zero.
If the acceleration of the object is zero the kinematics equation yields:
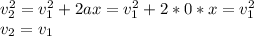
Then if we plug this into the work energy theorem