Complete question:
An ideal gas is slowly compressed at a constant pressure of2.0 atm from 10.0 L to 2.0 L, path B to D in Fig 19-12. If the heat lost from the gas in the process BD is
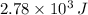 , what is the change in internal energy of the gas?
, what is the change in internal energy of the gas?
(The missing figure is attached below)
Answer:
The change in internal energy of the gas is -1158.8 joules
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve this problem we're going to use the first law of thermodynamics, that states the change in the internal energy of a system
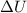 is the sum of the heat
is the sum of the heat
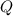 and the work
and the work
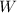 :
:
[tex\Delta U=W+Q [/tex] (1)
The heat lost in BD is
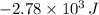 and because it is lost has negative sign, the work is the area under the curve BD that is a rectangle with length
and because it is lost has negative sign, the work is the area under the curve BD that is a rectangle with length
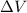 and height
and height
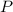 , using those on (1)
, using those on (1)
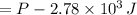
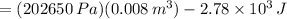
(8L=0.008
 and 2.0 atm =202650 Pa )
and 2.0 atm =202650 Pa )
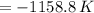
That means internal energy decreses.