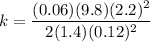Answer:
K=70.58 Nw/m
Step-by-step explanation:
Conservation Of The Energy
When no losses are considered, like friction or air resistance, the total energy present in a system is constant. Three types of energy are commonly used in simple physics applications:
Kinetic energy:
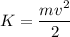
Potential gravitational energy:
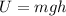
Elastic potential energy
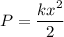
The variables used in the formulas are: m=mass, v=speed, h=height above ground, g=acceleration of gravity, k=spring constant, x=spring compression
When the spring is compressed, the ball is at rest, and only two energies are present, the elastic and the potential. Thus
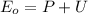
After the trigger is pressed, all the elastic energy is released and transformed in kinetic and the ball is fired at speed
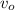 . At this moment, the ball has two energies: Kinetic and potential. The potential energy is the same as before because the ball is still at the same height, so
. At this moment, the ball has two energies: Kinetic and potential. The potential energy is the same as before because the ball is still at the same height, so
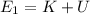
Equating both energies
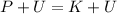
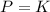
Or equivalently
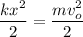
Rearranging
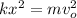
Solving for k
![\displaystyle k=(mv_o^2)/(x^2).......[1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/ofzyzwtf1nqnesz4l5t8wlzdk3vx8vc2pc.png)
We need to find
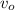 by using motion conditions. We know the ball reaches a distance d=2.2 m after traveling height of h=1.4 m. We can use these data to find
by using motion conditions. We know the ball reaches a distance d=2.2 m after traveling height of h=1.4 m. We can use these data to find
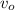 .
.
The horizontal distance is given by
![d=v_o.t..........[2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/cby5xz70wcn7p939oiaeq9wuyovv9lhnh6.png)
The vertical height is
![\displaystyle h=(gt^2)/(2)...........[3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/ni2yruu95f1io5up9dxko40ms2r0d0wmjn.png)
Solving for t in [2]
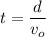
Replacing in [3]
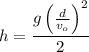
Operating
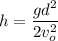
Solving for
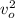
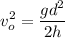
Replacing in [1]
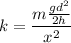
Rearranging
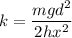
Computing with m=60 gr= 0.06 Kg, x=12 cm = 0.12 m