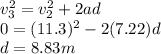Answer:
a) v = 11.3 m/s
b) d = 8.83 m
c) v = 11.3 m/s and d = 8.83 m
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The work-energy theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the object.
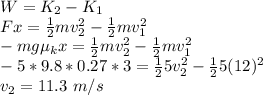
b) We will use the conservation of energy.
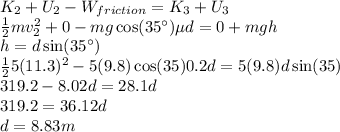
c) Newton’s Second Law will be applied.
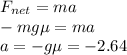
The final speed can be found by using the kinematics equations:
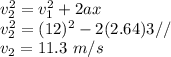
Similarly,
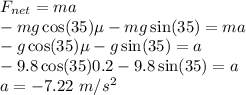
The kinematics equations are