Answer:
a)
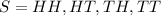
b)
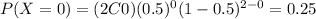
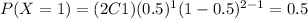
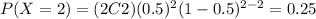
And we have the following table:
X | 0 | 1 | 2
P(X) | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25
Explanation:
Let's define first some notation
H= represent a head for the coin tossed
T= represent tails for the coin tossed
We are going to toss a coin 2 times so then the size of the sample size is
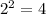
a. What is the sample space for this chance experiment?
The sampling space on this case is given by:
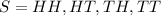
b. For this chance experiment, give the probability distribution for the random variable of the total number of heads observed.
The possible values for the number of heads are X=0,1,2. If we assume a fair coin then the probability of obtain heads is the same probability of obtain tails and we can find the distribution like this:
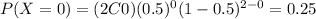
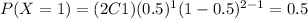
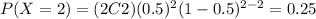
And we have the following table:
X | 0 | 1 | 2
P(X) | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25