Answer: a) The rate constant, k, for this reaction is
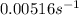
b) No
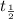 does not depend on concentration.
does not depend on concentration.
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
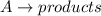
Given: Order with respect to
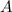 = 1
= 1
Thus rate law is:
a)
![Rate=k[A]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/nko3xnq7zjriz4tagxj1kmaw2dpgtm0bkn.png)
k= rate constant
![0.00250=k[0.484]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/wo8u90lb2a74ybdr7hwy2m2c3n89rtm9cp.png)
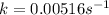
The rate constant, k, for this reaction is
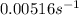
b) Expression for rate law for first order kinetics is given by:
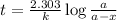
where,
k = rate constant
t = age of sample
a = let initial amount of the reactant
a - x = amount left after decay process
Half life is the amount of time taken by a radioactive material to decay to half of its original value.
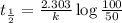
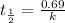
Thus
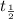 does not depend on concentration.
does not depend on concentration.