Answer:
Approximately
 .
.
Assumption: air resistance is negligible.
Step-by-step explanation:
Make sure all the values are in standard units.
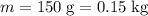 .
.
The bounce here is an inelastic collision between the ball and the surface. Some of the kinetic energy (KE) was lost. The exact value of energy loss would be equal to
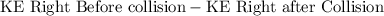 .
.
Before the bounce, all the kinetic energy of the ball would come from the drop from
 . That is:
. That is:
 .
.
After the bounce, the ball travels to a height of
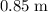 . All the potential energy gained in that process should come from the kinetic energy when the ball bounces back from the ground.
. All the potential energy gained in that process should come from the kinetic energy when the ball bounces back from the ground.
 .
.
Hence, the size of energy loss due to the bounce would be equal to
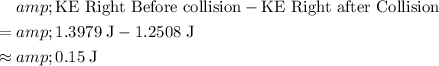 .
.