Answer:
a) 26.65 kJ was the heat evolved by the reaction.
b)
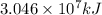 is the energy released on burning 1 metric ton of this type of coal
is the energy released on burning 1 metric ton of this type of coal
Step-by-step explanation:
Heat capacity of the calorimeter = C = 20.5 kJ/°C
Initial temperature of the calorimeter,
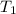 = 22.50°C
= 22.50°C
Final temperature of the calorimeter,
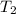 = 23.80°C
= 23.80°C
The heat evolved by the reaction = Q
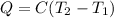
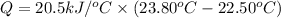
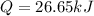
26.65 kJ was the heat evolved by the reaction.
0.875 g sample of anthracite coal was burned in a bomb calorimeter
0.875 g sample of anthracite coal gives 26.65 kJ of heat.
1 metric ton= 1000 kg
1000 kg = 1000 × 1000 g = 1,000,000 (1 kg =1000 g)
Then burning 1,000,000 g coal will give:
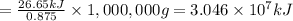
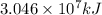 is the energy released on burning 1 metric ton of this type of coal
is the energy released on burning 1 metric ton of this type of coal