Answer:
their momenta are opposite but equal
Step-by-step explanation:
Given are masses of a Russian cosmonaut and a USA astronaut in the sequence,
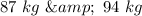
They are motionless initially and floating in the space without any friction.
- When they face each other and push each other palm to palm they execute a perfectly elastic collision.
- Since the collision is perfectly elastic no part of the mechanical energy will convert into any other form of energy and the whole will contribute to the mechanical energy of the system.
- So according to the Newtons second law there will act an equal amount of force in opposite direction on both the bodies after they push each-other.
According to the law of conservation of linear momentum of this system the sum of initial momentum will be equal to the sum of final momentum of the bodies.
Mathematically:
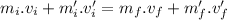
∵since the bodies are initially at rest.
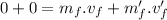
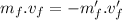
where the negative sign denotes the opposite direction.