Answer:
![f(x) = (1-e^{-(1)/(2)x})[-e^(-x) +e^0]=(1-e^{-(x)/(2)})[1-e^(-x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/geecifn5bho94ydtqsvjxe1howtyi89ghv.png)
Explanation:
If we have two random variables Y1 and Y2 and we have th following limits:
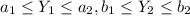
We an find the density function with this formula:
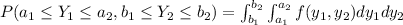
Now for our problem we know that for the two times of failure the density function is given by:
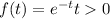
And we know that the joint density for T1 and T2 is given by:
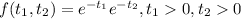
And we know that
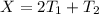
If we solve for
![T_1[/tex we got:</p><p>[tex] T_1 =(X-T_2)/(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/itag2e7hglx4d45jafcsd8bty5ypqkqxst.png)
And then we can find the density function like this:
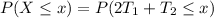
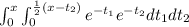
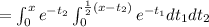
![=\int_(0)^x e^(-t_2) [-e^(-t_1) \Big|_0^{(1)/(2)(x-t_2)}] dt_2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/9mvxhjg33toiju30tfgc973zr65kzo7b5f.png)
![=\int_(0)^x e^(-t_2) [1-e^{-(1)/(2) (x-t_2)}] dt_2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/959ujaonvs33nze8swa6oj89kydegtpfw1.png)
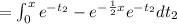
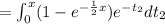
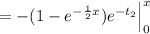
![f(x) = (1-e^{-(1)/(2)x})[-e^(-x) +e^0]=(1-e^{-(x)/(2)})[1-e^(-x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/geecifn5bho94ydtqsvjxe1howtyi89ghv.png)