Answer:
The kinetic energy is the same as in space, which in general is very large
Step-by-step explanation:
If the Earth had no atmosphere we can use the conservation of kinetic energy in two points
Initial. In space far from the planet
Em₀ = k = ½ m v₀²
Final. Just before touching the surface of the Earth
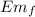 = K = ½ m v²
= K = ½ m v²
As there is no rubbing
Em₀ =
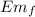
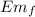 = ½ m v₀²
= ½ m v₀²
The kinetic energy is the same as in space, which in general is very large
When the Earth has an atmosphere we must use the energy work theorem
W = ΔK
The work is done by the friction forces when the meteor enters the atmosphere, increases in density as it approaches the surface, so the work also increases.
W =
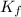 - K₀
- K₀
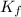 = K₀ - W
= K₀ - W
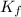 = ½ m v₀² - W
= ½ m v₀² - W
We see that the kinetic energy decreases as the work increases, this makes the impact is higher and part of the meteor also evaporates by friction at the entrance