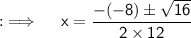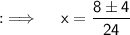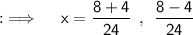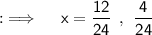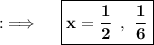We are given with a quadratic equation, but before solving the equation, let's convert it to the standard form of a quadratic equation i.e ax² + bx + c = 0 first ;
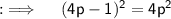
Using the identity (a - b)² = a² + b² - 2ab, we will be having
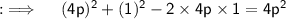
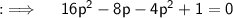
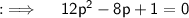
So, now if we compare it with the standard form of quadratic equation, we will be having a = 12, b = -8 and c = 1, so now Discriminant (D) = b² - 4ac = (-8)² - 4 × 12 × 1 = 64 - 48 = 16, now as D > 0, so two real and distinct roots exist, so now by quadratic formula we know that ;
So, now solving for x, we will be having ;