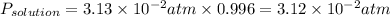Answer:
3.12 × 10⁻² atm
Step-by-step explanation:
A student dissolves 20.0 g of glucose into 511 mL of water. At 25 °C, the vapor pressure of pure water at 25 C is 3.13 × 10⁻² atm. I think the question is: "What is the vapor pressure of the solution?"
According to Raoult's law, the vapor pressure of a solvent above a solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure solvent times the mole fraction of the solvent present.
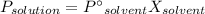
The molar mass of glucose is 180.16 g/mol. The moles corresponding to 20.0 g of glucose are:
20.0 g × (1 mol/180.16 g) = 0.111 mol
The density of water at 25°C is 0.997 g/mL. The mass corresponding to 511 mL of water is:
511 mL × (0.997 g/mL) = 509 g
The molar mass of water is 18.02 g/mol. The moles corresponding to 509 g of water are:
509 g × (1 mol/18.02 g) = 28.2 mol
The total number of moles is 0.111 mol + 28.2 mol = 28.3 mol
The mole fraction of water is:
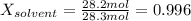
The vapor pressure of a solvent above the solution is: