Answer :
The final pressure of gas will be, 3.92 atm
The original volume of gas is, 17.46 L
The number of moles of argon gas added is, 0.57 mol.
Explanation :
Part 1 :
Combined gas law is the combination of Boyle's law, Charles's law and Gay-Lussac's law.
The combined gas equation is,
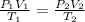
where,
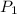 = initial pressure of gas = 3.00 atm
= initial pressure of gas = 3.00 atm
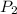 = final pressure of gas = ?
= final pressure of gas = ?
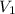 = initial volume of gas = 1.40 L
= initial volume of gas = 1.40 L
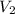 = final volume of gas = 0.950 L
= final volume of gas = 0.950 L
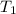 = initial temperature of gas =
= initial temperature of gas =
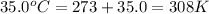
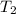 = final temperature of gas =
= final temperature of gas =
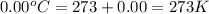
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get:
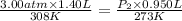
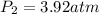
Therefore, the final pressure of gas will be, 3.92 atm
Part 2 :
First we have to calculate the original volume of gas.
Using ideal gas equation:
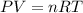
where,
P = pressure of gas = 65.0 kPa
V = volume of gas = 3.06 L
T = temperature of gas =
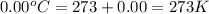
n = number of moles of gas = 0.500 mol
R = gas constant = 8.314 kPa.L/mol.K
Now put all the given values in the ideal gas equation, we get:
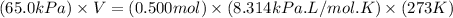
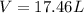
Now we have to calculate the final moles of sample of gas.
Using ideal gas equation:
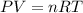
where,
P = pressure of gas = 45.0 kPa
V = volume of gas = 60.0 L
T = temperature of gas =
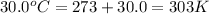
n = number of moles of gas = ?
R = gas constant = 8.314 kPa.L/mol.K
Now put all the given values in the ideal gas equation, we get:
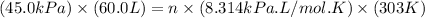
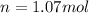
Now we have to calculate the number of moles of argon gas added.
Moles of argon gas added = Final moles of gas - Initial moles of gas
Moles of argon gas added = 1.07 mol - 0.500 mol
Moles of argon gas added = 0.57 mol
Thus, the number of moles of argon gas added is, 0.57 mol.