Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate that you need to know the value of the Kps (constant of solubility) at 30°C of KBr in water.
When the product of the concentrations of both ions (Br- and K+) equals the Kps, the solution is saturated.
Given the disociation of the salt in water:
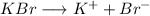
The concentration of both ions are equal (1:1 ratio) and the same as the concentration of KBr added.
The Kps:
![Kps=[K^+][Br^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/efwvycloubhpus9b1796wofe75x9amesho.png)
![[KBr]=(Kps)^(1/2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/m46s0cz40rb516syoc9o0l049d1qb99s4p.png)
[KBr] are moles of the salt per litre of water
Assuming a density of water of 1 g/cm3, 100 g are 0.1 litre
To calculate the mass:
![m=[KBr]*M*0.1 litre](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/bqwcbeydmrhic8d99g7xpilfjw4ex03kb8.png)
where M is the molecular weight of the salt.