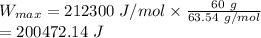Answer:
Max. work done in 60 g of copper plated out is 200472.14 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Given cell reaction is:
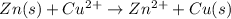
Standard reduction potential of Zn electrode (
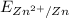 ) is 0.763 V.
) is 0.763 V.
Standard reduction potential of Cu electrode (
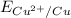 ) is -0.337 V.
) is -0.337 V.
Copper acts as cathode and Zinc acts as anode.
Cell potential (E) = E° cathode - E° anode
= 0.763 - (-0.337)
= 1.10 V
formula for the work done is as follows:

Here, n is no. of electron involved in the reaction.
F(Faraday's constant) = 96500
In the given reaction, n = 2
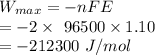
Therefore, 212300 J work is done by reducting 1 mol of copper.
Copper given is 60 g.
Molecular mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol.
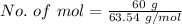
Max. work done in 60 g of copper plated out is: