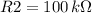Complete question:
In the circuit shown in the figure below (See image attached), suppose that the value of R1 is
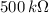 . To obtain a multimeter reading of 1 V between points B and C in the circuit, the value of R2 would have to be.
. To obtain a multimeter reading of 1 V between points B and C in the circuit, the value of R2 would have to be.
Answer:
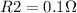
Step-by-step explanation:
First, we are going to the find current trough the circuit, because the resistors are on series the current is the same on each resistor so I=I1=I2. The Ohm's law for the circuit is:
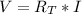 (1) , with V the voltage of the battery (6V), I the current trough the circuit and
(1) , with V the voltage of the battery (6V), I the current trough the circuit and
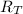 the total resistance of the circuit, but for resistors on series the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistance so
the total resistance of the circuit, but for resistors on series the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistance so
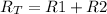 (2).
(2).
Using (2) on (1) and solving for I:
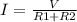 (3)
(3)
Ohm's law is true for the individual resistors too so we're going to apply that on R2:
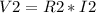 , but remember I2=I
, but remember I2=I
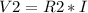 (4), using (3) on (4)
(4), using (3) on (4)
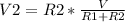 , solving for R2:
, solving for R2:
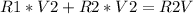
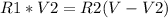
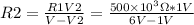 , V2= 1V because we want that reading on the multimeter.
, V2= 1V because we want that reading on the multimeter.