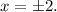Explanation:
To find the maxima/minima of a function, we solve for the derivative of the given function
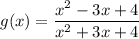
Recall that according to the quotient rule of differentiation, if a function g(x) is defined as a ratio of two functions f(x) and h(x), then the derivative of g(x) is
![g'(x) = (f'(x)h(x) - f(x)h'(x))/([g(x)]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/kh98k76tyviingqi7flxc6i4sp11kqh3z9.png)
Let
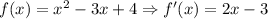
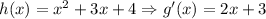
The derivative g')x) is then
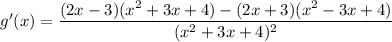
Carrying out the multiplication and collecting all similar terms, we arrive at
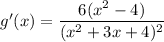
The maxima/minima of the function g(x) occurs where g'(x) = 0 and this happens when the numerator of g'(x) is
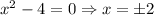
Look at the graph above. The blue line represents the function g(x) and the red line is for the derivative of g(x) and you can clearly see that maxima/minima occurs when the red line intersects the horizontal axis, i.e., becomes zero at