Answer:
A. 2/(1 -x)²
Explanation:
The derivative of a ratio is given by the formula ...
d(u/v) = (v·du =u·dv)/v²
Here, we have ...
u = 1+x; du = 1·dx
v = 1 -x; dv = -1·dx
Then ...
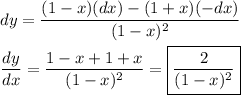
__
Additional comment
The formula used above is a combination of the power rule and the product rule.
- d(u^-1) = -du·u^-2 = -du/u² . . . . power rule
- d(uv) = u·dv +v·du . . . . . . . . product rule