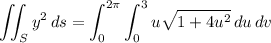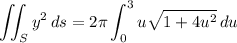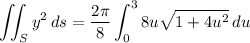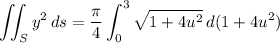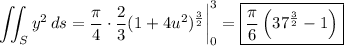Parameterize S in cylindrical coordinates by the vector function
r(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v))
with
x(u, v) = u cos(v)
y(u, v) = u sin(v)
z(u, v) = 36 - u²
with 0 ≤ u ≤ 3 and 0 ≤ v ≤ 2π. Take the normal vector to S to be
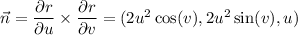
so that the surface element is
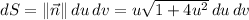
Then the surface integral is