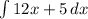
For this problem, let's first apply the intergral sum rule.
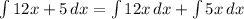
Then, we'll use the reverse power rule on each of these integrals.
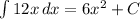
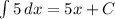
So the indefinite integral of
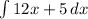 is
is
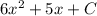 .
.
Remember that we need our constant of integration,
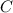 , because of if we take the derivative of a constant, it'll be 0.
, because of if we take the derivative of a constant, it'll be 0.
Hope this helps!