Answer:
Discriminant is -20 (D<0, no real roots)
Explanation:
The Discriminant Formula:
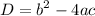
First, arrange expression in the standard form or ax^2+bx+c = 0.
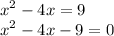
From above, we subtract both sides by 9.
Compare the coefficients:
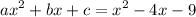
Substitute a = 1, b = -4 and c = -9 in the formula.
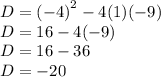
Therefore the discriminant of equation is -20 which is less than 0.