Answer:
-7
Explanation:
In the equation of ax² +bx +c= 0, the discriminant (denoted by D) is
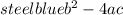 .
.
-2x² -x -1= 0
Let's identify the values of a, b and c in this equation! It is important to account for the negative sign too.
a= -2, b= -1, c= -1
D
= (-1)² -4(-2)(-1)
= 1 -4(2)
= 1 -8
= -7
Implications of discriminant
- The discriminant tells us the number of roots (solutions) the equation has
- When D < 0, there are no real roots
- When D= 0, there is one real root
- When D > 0, there are two real roots