Step-by-step explanation:
We start by using the conservation law of energy:

or
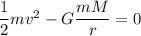
Simplifying the above equation, we get
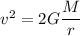
We can rewrite this as
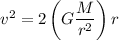
Note that the expression inside the parenthesis is simply the acceleration due to gravity
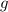 so we can write
so we can write
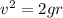
where
 is the launch velocity.
is the launch velocity.