We are given with an integral and need to solve the integral , so let's start ;
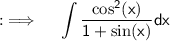
As we know that sin²(x) + cos²(x) = 1 , using this
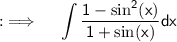
Can be further written as
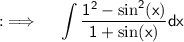
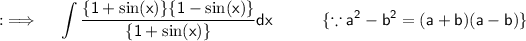
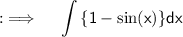
Now , as integrals follow distributive property , so ;
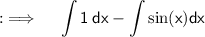
Now , as antiderivative (Integration) of sin(x) is -cos(x) + C and that of dx is x + C So ;
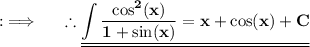
This is the Required answer